Peerless What Is Feasibility Study Explain Its Types

Determines whether the relevant technology is stable and established.
What is feasibility study explain its types. The result of feasibility study also determines whether the solution for the problem should be implemented. As the name implies a feasibility study is an analysis into the viability of an idea. Feasibility Study in Software Engineering is a study to evaluate feasibility of proposed project or system.
Feasibility studies help answer the essential question should we proceed with the proposed idea The objective study may be completed. It is an important task in project management that every project must go through at one stage or another before going on any further steps towards its development. Its Types and How to Write.
A feasibility study is an assessment of the practicality of a proposed plan or project. It is measure of how well the solution will work in the organization. The aim of the feasibility study is to understand the problem and to determine whether it is worth proceeding.
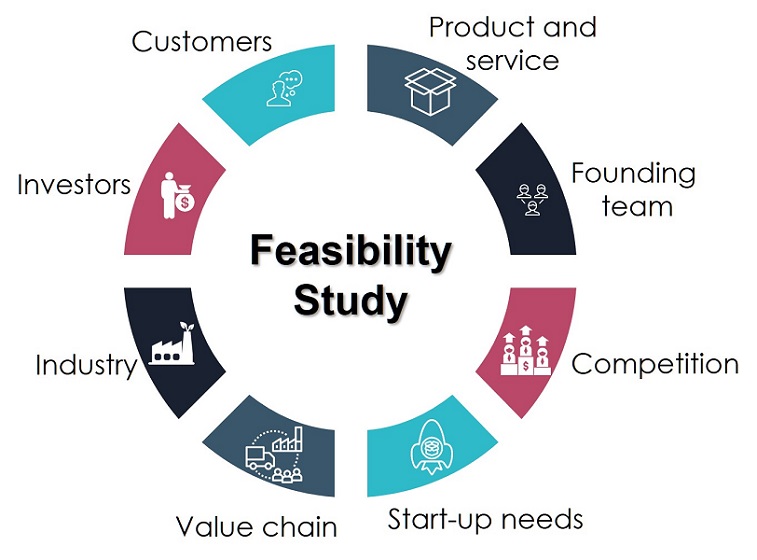
An analysis and evaluation of a proposed project to determine if it 1 is technically feasible 2 is feasible within the. The feasibility study is not merely a project research but a framework or a plan on how to establish and run business successfully in the long run. Which helps to find the strengths and weaknesses of an existing business or proposed venture opportunities and threats present in the environment the resources required to carry through and ultimately the prospects for success.
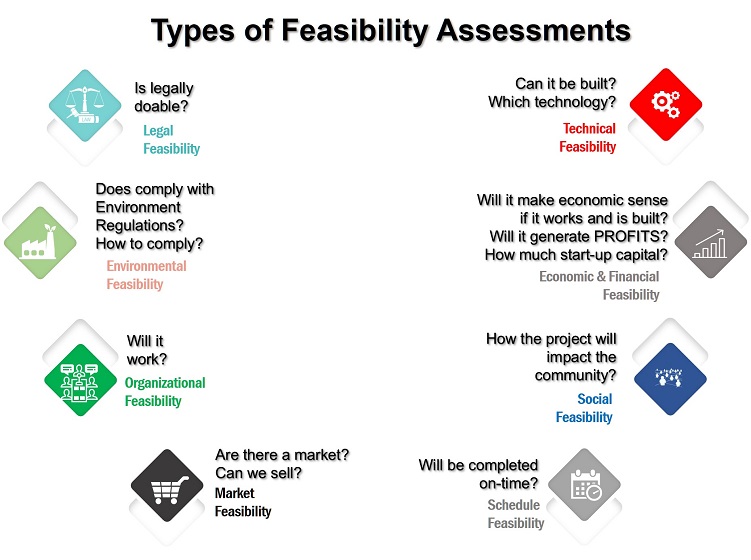
This is known as feasibility study. It is the measure of the practicality of a specific technical solution and the availability of technical resource and expertise. It ensures that a project is legally and technically feasible and economically justifiable.
Written 52 years ago by ramnath 81k. It is the measure and the study of how beneficial the development of the system would be to the organization. The document is intended for the systems stakeholder someone who has some direct or indirect.